Joint pain
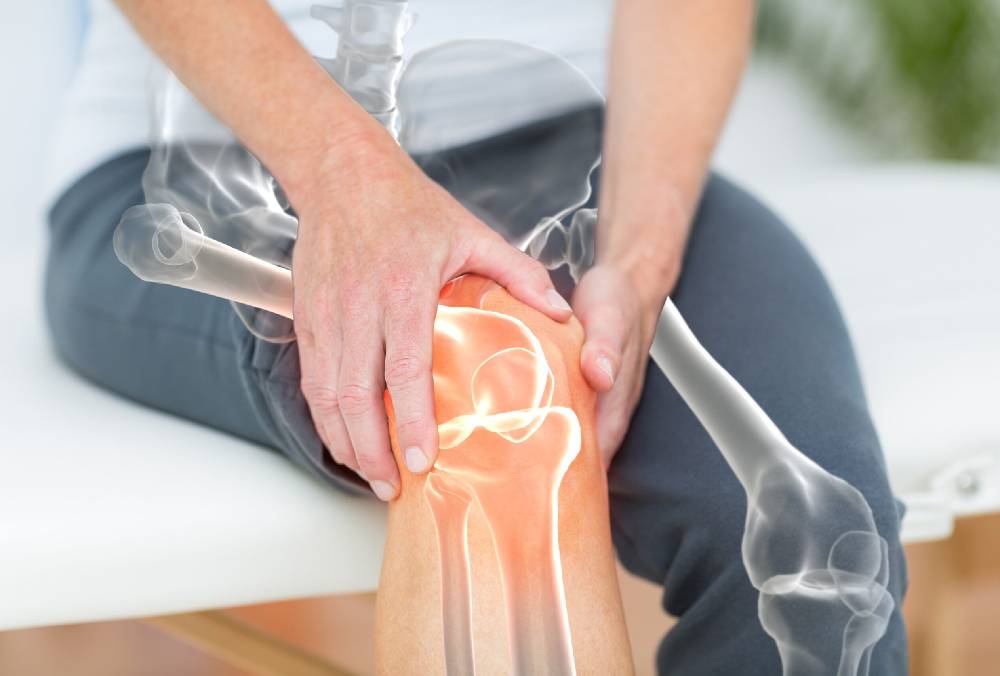
What is Joint Pain?
Joint pain, also known as arthralgia, refers to discomfort, soreness, or stiffness in any of the body’s joints, where two or more bones meet. Joints are essential for movement, and when they become inflamed, damaged, or affected by disease, it can lead to pain, swelling, and limited mobility. Joint pain can occur in any joint in the body, including the knees, hips, shoulders, elbows, wrists, and fingers. It can range from mild to severe and may be accompanied by other symptoms like swelling, warmth, or redness around the affected area.
Joint pain is often a result of injury, overuse, or an underlying medical condition such as arthritis or bursitis. It can affect people of all ages and can be acute (short-term) or chronic (long-term). Seeking proper medical attention and treatment is crucial for managing joint pain and improving the quality of life.
Joint pain is often a result of injury, overuse, or an underlying medical condition such as arthritis or bursitis. It can affect people of all ages and can be acute (short-term) or chronic (long-term). Seeking proper medical attention and treatment is crucial for managing joint pain and improving the quality of life.
Causes :
Joint pain can be caused by a variety of factors, ranging from everyday wear and tear to underlying health conditions. Some of the most common causes of joint pain include:
- Osteoarthritis: The most common form of arthritis, osteoarthritis occurs when the protective cartilage at the ends of the bones deteriorates over time, causing pain, swelling, and stiffness in the affected joints.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks the synovial lining of the joints, leading to inflammation, pain, and potential joint deformity.
- Injuries: Traumatic injuries such as fractures, sprains, or strains can damage the bones, cartilage, ligaments, or tendons in a joint, leading to pain and swelling.
- Gout: A type of arthritis caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints, usually in the big toe, resulting in intense pain, redness, and swelling.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursae (fluid-filled sacs that cushion the joints), often caused by repetitive movements or overuse, leading to joint pain and stiffness.
- Tendinitis: Inflammation of the tendons around the joint, often due to overuse or repetitive motions, causing pain and limited mobility.
- Lupus: An autoimmune disease that can affect joints, causing inflammation, pain, and damage to the joints over time.
- Infections: Infections like septic arthritis can lead to severe joint pain, swelling, and fever, requiring immediate medical attention.
- Overuse or Strain: Repetitive motion or overuse of a joint can lead to inflammation and pain, especially in athletes or people with physically demanding jobs.
Symptoms :
The symptoms of joint pain can vary depending on the underlying cause, but common symptoms include:
- Pain: Varies in intensity from dull aches to sharp, stabbing pain, often made worse by movement or pressure.
- Swelling: Joint swelling often accompanies inflammation and may make the joint appear larger or feel “puffy.”
- Stiffness: Difficulty moving the joint, especially after periods of rest, such as first thing in the morning.
- Redness and Warmth: Inflamed joints may appear red and feel warm to the touch, indicating inflammation or infection.
- Decreased Range of Motion: Limited ability to move the joint fully, which can affect daily activities such as walking, bending, or reaching.
- Tenderness: The joint may feel tender or sore when touched, especially during flare-ups.
- Joint Instability: A feeling that the joint may “give way” or become unstable, especially if the ligaments or tendons are involved.
The Approach to Joint Pain
The approach to treating joint pain depends on the underlying cause, the severity of the pain, and the patient’s overall health. The treatment process typically involves a combination of the following:
- Diagnosis: The first step in addressing joint pain is a thorough medical evaluation. This includes taking a detailed history, conducting a physical examination, and ordering diagnostic tests like X-rays, MRI scans, blood tests, or joint fluid analysis to determine the cause of the pain.
- Pain Management: Pain relief is often the primary goal in the early stages of treatment. This may involve over-the-counter pain relievers (such as acetaminophen or NSAIDs), prescription medications, or corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
- Physical Therapy: Rehabilitation exercises are commonly recommended to improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the affected joint. Physical therapy can help reduce pain, prevent further damage, and restore joint function.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Maintaining a healthy weight, using proper posture, and avoiding overuse of the affected joint can significantly reduce stress and strain on the joint, helping to prevent further pain and damage.
- Surgical Interventions: In some cases, if conservative treatments fail to provide relief, surgery may be recommended. Options include joint repair or replacement surgery, depending on the severity of the condition. Arthroscopy, a minimally invasive procedure, may also be used to clean out damaged tissue or repair joint damage.
- Alternative Treatments: Some patients find relief through complementary therapies, such as acupuncture, massage, or dietary supplements (such as glucosamine and chondroitin) to support joint health.
- Preventive Measures: In cases where joint pain is linked to conditions like osteoarthritis, taking preventive measures such as regular exercise, proper joint care, and nutritional supplements can help slow the progression of joint damage.
Our Process for Joint Pain Treatment
At our Hospital, we are committed to helping you manage and treat joint pain with a comprehensive, patient-centered approach. Our process includes:
- Comprehensive Consultation: We begin with a thorough consultation to understand your symptoms, medical history, and lifestyle. This helps us determine the most appropriate course of treatment. We listen to your concerns and tailor our approach to meet your unique needs.
- Accurate Diagnosis: Using advanced diagnostic tools, including imaging and lab tests, we accurately diagnose the underlying cause of your joint pain. Whether it’s due to arthritis, injury, or another condition, knowing the exact cause is essential for effective treatment.
- Personalized Treatment Plan: Based on your diagnosis, our team will develop a personalized treatment plan that may include a combination of pain management, physical therapy, lifestyle changes, and in some cases, surgical options. We focus on treating the root cause of your pain, not just the symptoms.
- Non-Surgical Interventions: For many patients, non-surgical treatments such as physical therapy, medications, and injections are effective in reducing pain and improving joint function. We also emphasize self-care techniques to help you manage pain at home, such as rest, ice, heat therapy, and exercises.
- Advanced Surgical Options: If your joint pain is caused by severe arthritis, a major injury, or joint degeneration, we offer advanced surgical options such as arthroscopy, joint repair, or joint replacement. Our experienced surgeons will explain all the available options and help you make the best decision for your health.
- Ongoing Support and Rehabilitation: After treatment, we provide ongoing support to ensure that you continue to heal and regain full function. Our rehabilitation programs are designed to help you recover fully and prevent future joint problems. We monitor your progress and make adjustments to your treatment plan as needed.
- Long-Term Care and Prevention: We believe in preventive care and offer regular check-ups and monitoring to prevent joint pain from recurring. Our team will provide advice on lifestyle modifications, exercise routines, and nutrition to help you maintain joint health for the long term.
